Often considered the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D is crucial to maintaining overall health. But what happens when your body doesn’t get enough of it? This blog post explores vitamin D deficiency, its symptoms, common causes, and dietary solutions to get your vitamin D levels back on track.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D, a crucial fat-soluble nutrient, plays a key role in bone health by aiding calcium absorption. It is found in food, beverages, and supplements in two forms: D2 and D3. While both raise vitamin D levels, D3 might be more effective for long-term stores. Interestingly, sunshine exposure is the primary way humans acquire vitamin D, but certain factors and conditions can increase the risk of deficiency.
Importance of Vitamin D
Beyond its bone-building benefits, vitamin D offers a broader range of health advantages. It helps prevent osteoporosis, a declining bone mass and density. Research also suggests a link between abnormal vitamin D levels and a high risk of certain cancers. Additionally, vitamin D plays a role in maintaing the immune system. When vitamin D levels are insufficient, the risk of autoimmune diseases, where the body attacks its tissues, can rise.
How Common Is Vitamin D Deficiency?
Despite its nickname, the “sunshine vitamin,” vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly widespread and doesn’t solely stem from a lack of sun exposure. Factors like underlying health conditions, skin pigmentation, and even age can hinder our ability to get the daily prescribed amount of vitamin D. In fact, it’s one of the most common vitamin deficiencies globally, with the National Library of Medicine estimating that a staggering 1 billion people worldwide have low vitamin D levels.
Causes of vitamin D deficiency
While sunshine exposure might make it easy to get enough vitamin D, several factors can contribute to deficiency. Underlying health conditions play a significant role. People with chronic kidney or liver disease may struggle to convert vitamin D into usable form. Digestive disorders like Crohn’s or Celiac disease can hinder absorption. Certain medications, particularly steroids, can also interfere. Even hormone imbalances, specifically parathyroid hormone levels that are too high or too low, can disrupt kidney vitamin D synthesis.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency
The sneaky thing about vitamin D deficiency is that it often goes unnoticed. People might not experience any symptoms for months or even years. However, that doesn’t mean there aren’t red flags to watch out for. Both physical and psychological symptoms can indicate a deficiency, making it crucial to be aware of these potential warnings.
- Physical Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
While vitamin D deficiency often goes unnoticed, there can be hidden signs. Frequent illnesses and infections might be a clue, as vitamin D helps keep your immune system strong. Bone pain and slow wound healing could also be indicators. Since vitamin D aids in reducing inflammation and creating new skin, a deficiency might hinder these processes. Even hair loss, particularly in women, has been linked to low vitamin D levels. Most importantly, a lack of vitamin D can contribute to bone loss due to its role in calcium absorption and health.
- Neurological Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
The warning signs of vitamin D deficiency can extend beyond the usual aches and pains. Some people experience a prickly “pins and needles” sensation in their hands and feet. Muscle weakness can make walking and moving difficult, and pain sensitivity might increase. There’s even emerging research suggesting a link between low vitamin D and neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis.
- Psychological Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
The impact of vitamin D deficiency can reach beyond physical symptoms. Some research suggests it can affect cognitive function and emotional well-being. People with low vitamin D levels might experience depressive symptoms, anxiety, and even mood swings. If you’re struggling with these issues, it’s worth checking your vitamin D levels, as addressing a deficiency could improve your mood and mental clarity.
Risk of vitamin D deficiency
Several factors can increase your risk of vitamin D deficiency. Like weight loss procedures, people who have undergone stomach surgeries may have trouble absorbing the vitamin. People with darker skin develop less vitamin D from sunlight, although research is ongoing to determine if this translates to the same health risks as in lighter skin tones. Certain medications, including steroids and cholesterol-lowering drugs, can hinder absorption. As we age, our skin’s ability to synthesize vitamin D declines. Breastfed infants are also at high risk since breast milk is low in vitamin D, and newborns shouldn’t get direct sunlight. Location plays a role, too; people living in areas with limited sunlight exposure are more likely to be deficient.
Vitamin D Deficiency in Older Adults
A combination of factors makes older adults particularly susceptible to vitamin D deficiency. Age itself reduces the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. On top of that, older people are more likely to have underlying health conditions that can worsen deficiency, such as diabetes, Crohn’s disease, and kidney disease. Reduced mobility and spending less time outdoors further limit sun exposure. Furthermore, dietary changes, like a lack of appetite or an imbalanced diet, can make obtaining enough vitamin D from food sources more complex. Some medications can also interact with the absorption and retention of the vitamin.

How Vitamin D Deficiency is Diagnosed
A blood test can check for vitamin D deficiency. The most common and reliable test measures 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in the blood. While vitamin D testing can be expensive and isn’t routinely recommended, it might be warranted for those who are at higher risk, such as older adults or people with certain health conditions.
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency
If you are facing vitamin D deficiency, there are ways to address it. In severe cases, a doctor might prescribe high-dose vitamin D supplements to raise levels quickly. Taking daily over-the-counter vitamin D supplements, often combined with magnesium to aid absorption, can be effective for milder deficiencies. Additionally, incorporating fortified foods like cereals, milk, and some orange juice into your diet can help you reach your daily vitamin D needs.
Source of vitamin D
Vitamin d drops
Vitamin D drops are an easy and reliable way for infants and young children to ensure they get enough of this essential nutrient. These drops are typically delivered orally and come in measured doses. As breast milk is deficient in vitamin D and sun exposure isn’t recommended for newborns, vitamin D drops can help prevent deficiency and support healthy bone development in little ones.
Vitamin d gummies
Vitamin D gummies offer a tasty and chewable alternative to traditional vitamin D supplements, especially for those who dislike swallowing pills. These gummies come in various flavours and dosages, making them a convenient option for adults and children. While generally less concentrated than prescription supplements, they can be a suitable way to boost vitamin D intake for those with mild deficiencies or who prefer a more enjoyable daily dose.
Liquid vitamin d
Liquid vitamin D provides another option for those with difficulty swallowing pills or capsules. It often comes in a dropper bottle for easy measurement and can be flavoured or unflavored. Like gummies, liquid vitamin D is typically less concentrated than prescription options. This can make it easier to adjust the dosage and ensure you get the right amount for your needs. However, you must consult your doctor before starting new supplements, including liquid vitamin D.
Foods to boost vitamin D
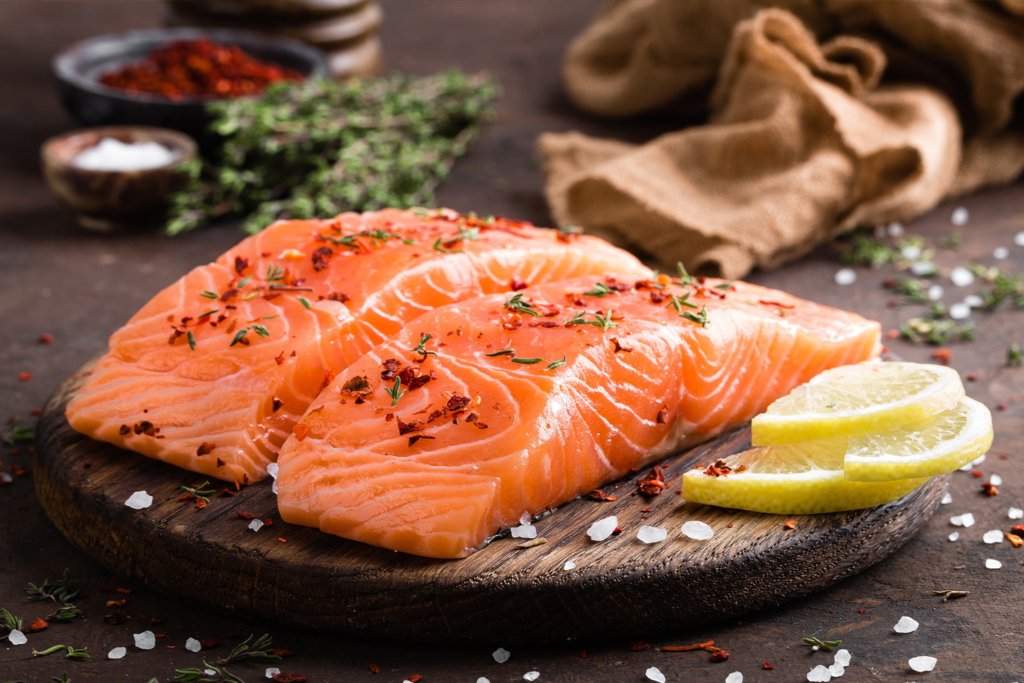
1. Salmon and fatty fish
Salmon is a champion for dietary vitamin D. This fatty fish is naturally rich in vitamin D, with a single serving offering a significant portion of your daily recommended intake. Wild-caught salmon tend to be higher in vitamin D compared to farm-raised varieties. So, if you’re looking for a delicious and nutritious way to boost your vitamin D levels, consider incorporating salmon into your meals.

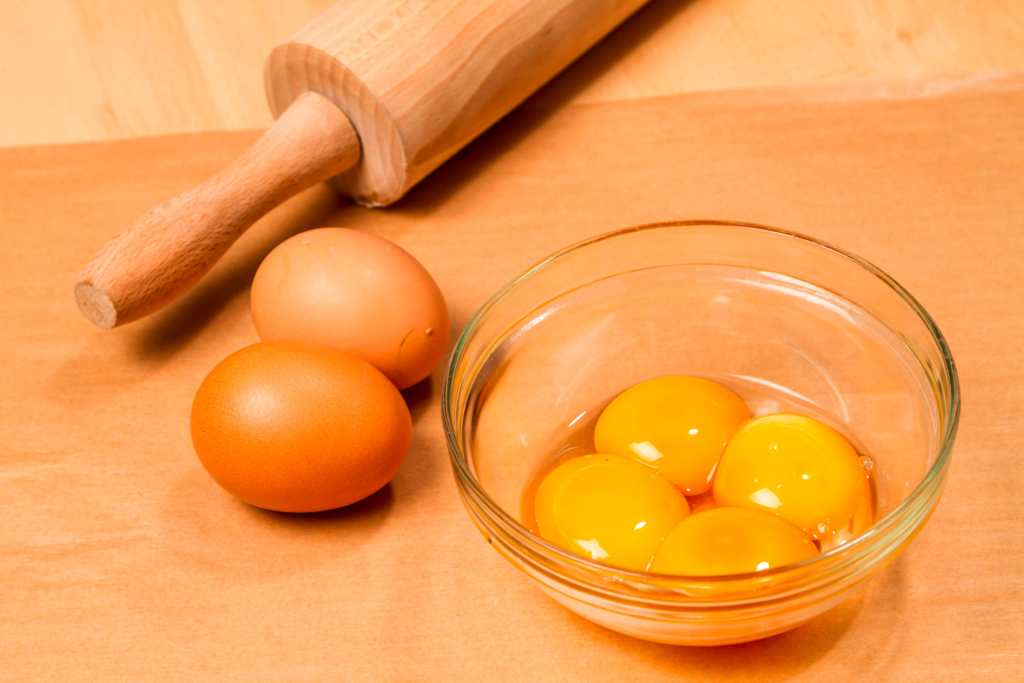
2. Egg yolks
Egg yolks, while not the richest source of vitamin D, can still contribute to your daily intake. Unlike the white, the yolk is where most of an egg’s nutrients reside, including a small amount of vitamin D. While it wouldn’t be enough to rely solely on eggs to meet your needs, incorporating them into your diet alongside other vitamin D sources can be a helpful strategy. This is especially beneficial for those who enjoy eggs and are looking for easy ways to boost their vitamin D intake.

3. Swordfish
Swordfish is another contender for the title of delicious source of vitamin D. A single serving boasts enough vitamin D to meet or even exceed daily recommendations. This makes it an excellent choice for those who enjoy seafood and seek ways to boost their vitamin D intake through dietary sources. However, it’s essential to be mindful of the potential mercury content in swordfish, especially for frequent consumption.

4. Beef liver
Though not as popular as other sources, beef liver packs a surprising punch of vitamin D. While not the most practical solution for daily intake due to its strong flavour, a serving of cooked beef liver can provide a significant amount of vitamin D, alongside other essential vitamins and minerals. This can be helpful for those looking to incorporate a wider variety of nutrient-rich foods into their diet to support healthy vitamin D levels.

FAQs
What is the fastest way to boost vitamin D?
While sunlight exposure can help raise vitamin D levels, the fastest way to boost them is with a high-dose prescription vitamin D supplement recommended by your doctor.
When should you see a doctor for a vitamin D problem?
The tricky part about vitamin D deficiency is that symptoms are often subtle and slow to appear. It can take years for the deficiency to manifest, and some signs can mimic other conditions. To navigate this, be mindful of your body. If you experience multiple symptoms like bone pain, frequent infections, or a low mood, see a doctor. Additionally, if you already know you have low vitamin D and experience new or worsening symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications.
Can Too Much Vitamin D Be Dangerous?
Achieving healthy vitamin D levels is essential, but moderation is key. While sun exposure won’t cause an overdose (your body regulates vitamin D production), excessive supplementation can lead to toxicity. Symptoms like nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, and confusion can arise. In severe cases, high vitamin D levels may cause kidney problems, irregular heartbeat, or even death.